
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in China Drops by 30% in Just One Year
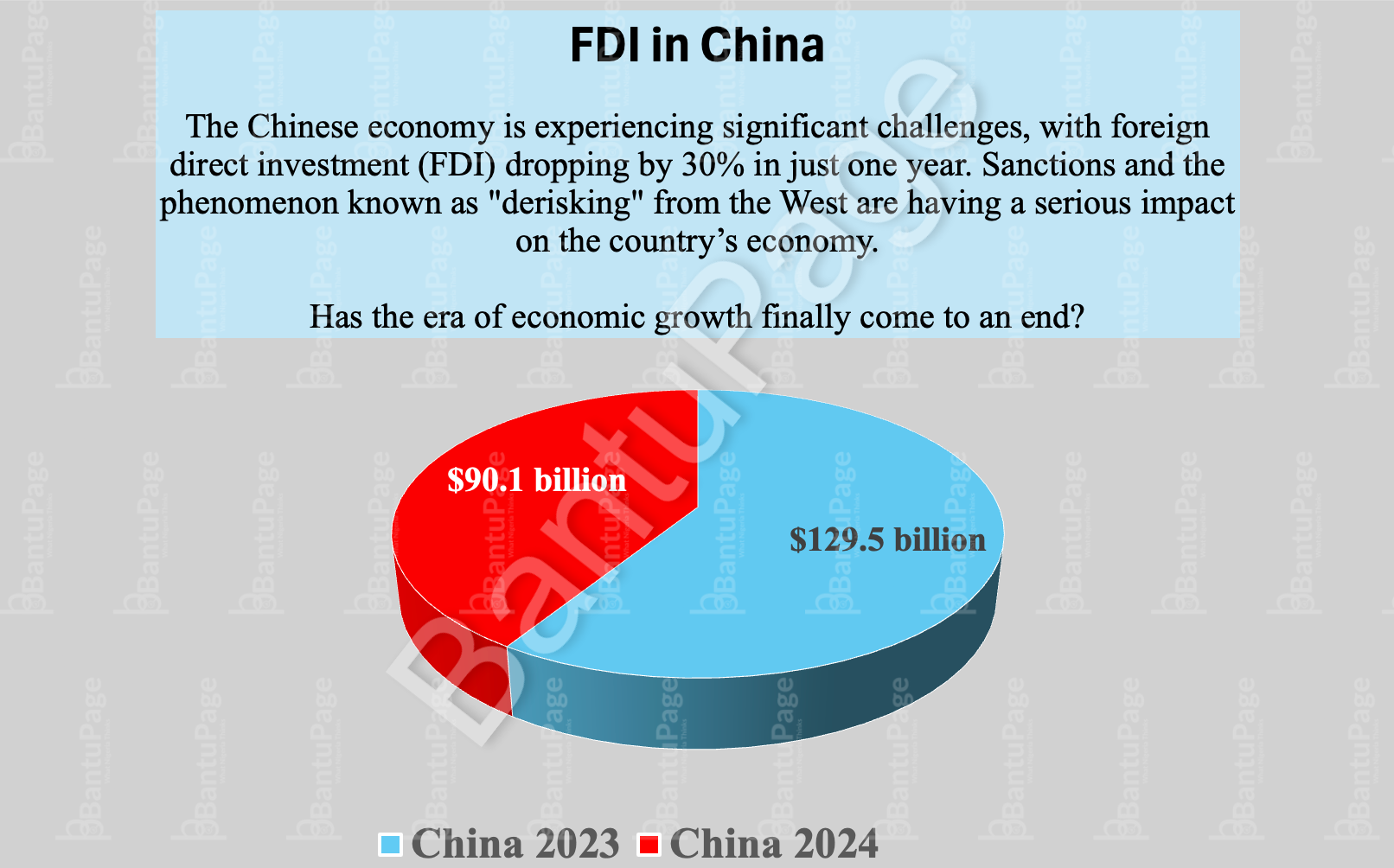
In 2023, China’s foreign direct investment (FDI) was $129.5 billion. However, a year later, in 2024, it fell by 30% to $90.1 billion, representing a decrease of $39 billion.
Western investors and companies are exiting China in large numbers. The concept of “derisking,” popularised in the West, may be negatively affecting the Chinese economy. Since the onset of COVID-19, China’s GDP has remained unchanged. While the US economy, valued at $26 trillion during the pandemic, has grown to nearly $29 trillion, China’s GDP has stagnated at $18 trillion since COVID-19.
In the first nine months of 2024, China saw the registration of 42,108 new foreign-invested firms, representing an 11% increase compared to the previous year. The country’s strength lies in its production capabilities, making it the world’s manufacturing superpower. However, if foreign direct investment (FDI) declines, investors may relocate, leading to a decrease in demand for Chinese goods, which would have significant economic repercussions. Compounding this issue is the declining competitiveness of the Chinese real estate sector, another critical component of the economy. It appears that the economy may face a prolonged period of slowdown.
Does this indicate the beginning of the end of the Chinese economic miracle?
By Ikechukwu ORJI







